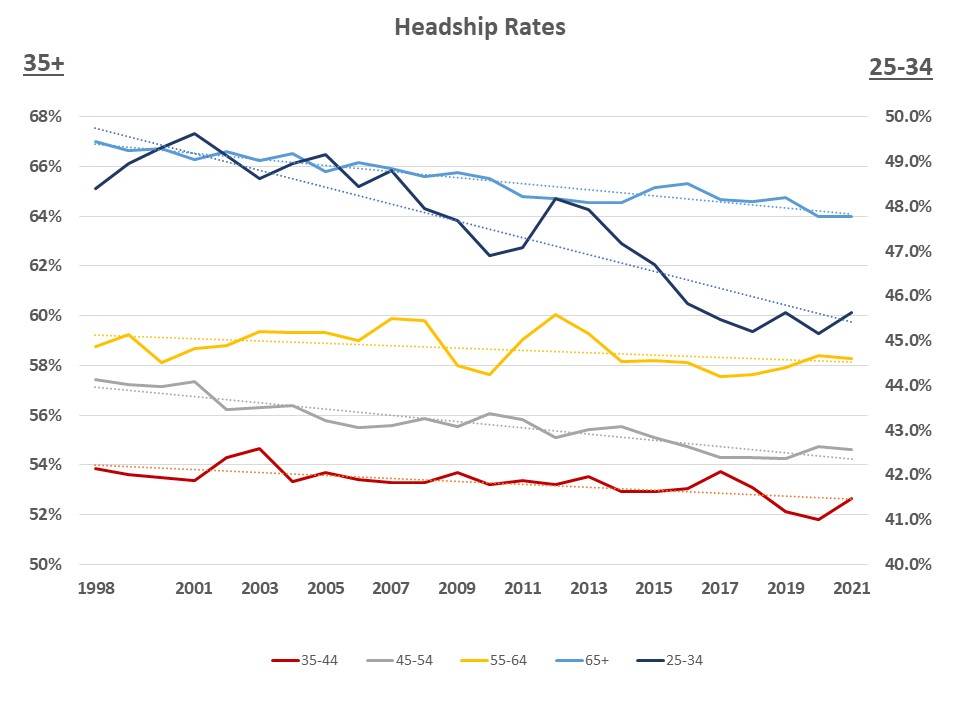
Headship rates for all age groups have been trending lower over the last two decades, with important implications for the demand for home building. The latest Current Population Survey (CPS) Annual Social and Economic Supplement (ASEC) data show that the pandemic housing boom brought this trend to a halt, with adults ages 35-64 now registering higher headship rates than they were pre-covid. For the younger group ages 25-34, headship rates bounced back to pre-pandemic levels. The only two age groups that saw a decline in their headship rates over the pandemic-fueled housing boom are college-age (18-24) adults and the 65+ cohort.
Headship rates – share of people who are household heads – tell us how many households are formed for a given population. The higher the headship rate, the more households are formed, the more housing units are occupied and the more housing is needed to be built. For decades, US headship rates have been declining, suggesting the US housing market has been missing millions of households and any gains in new households can be largely attributed to population growth.
This problematic trend was particularly pronounced among young adults ages 25-34. This group registered the steepest declines in their ability to create and lead independent households, highlighted by the 4 percentage point drop in their headship rates over the last two decades.
 Immediately before the Covid-19 pandemic, declining young adult headship rates reversed this trend and registered an uptick. At that time, it was a hopeful indicator that the troublesome trend of rising shares of young adults living with parents, relatives or sharing house with roommates finally reversed. Then, the rollercoaster 2020 and 2021 saw headship gains among young adults first eliminated early in the pandemic, only to be later restored to the pre-pandemic levels.
Immediately before the Covid-19 pandemic, declining young adult headship rates reversed this trend and registered an uptick. At that time, it was a hopeful indicator that the troublesome trend of rising shares of young adults living with parents, relatives or sharing house with roommates finally reversed. Then, the rollercoaster 2020 and 2021 saw headship gains among young adults first eliminated early in the pandemic, only to be later restored to the pre-pandemic levels.
It is worth noting that while headship rates for adults 35-64 years of age are now higher than they were before the Covid-19 pandemic, they remain historically low across every age group. It remains to be seen whether recent headship gains fueled by the pandemic housing boom can be sustained through the ongoing housing slowdown and probable recession.
The data used in this post come from the 2021 CPS ASEC. Typically, NAHB Economics relies on the American Community Survey (ACS) to estimate headship rates across all age groups. The ACS is less timely but has a much larger sample and aligns better with the Decennial Census. Even though the ACS estimates show lower headship rates across all age groups, the long-run trends are similar in both surveys. Because of data collection issues during the early pandemic, the 2020 ACS data are largely unreliable, and the 2021 data will only become available in the Fall of this year. In the interim, the CPS estimates provide an early indicator where the U.S. headship rates are heading.
Related