The Fraser Institute’s Economic Freedom of the World 2022 report was released this morning. This report covers 2020, which while most of our recent history is a bit of a blur, was the year when COVID-19 and COVID lockdowns defined our shared experience. The first of those lockdowns began in mid-March, and we spent most of the rest of 2020 figuring out how to negotiate a newly defined world. So whatever we end up seeing in the report, we’ll have to remember that we spent about 80 percent of 2020, for lack of a better word, grounded.
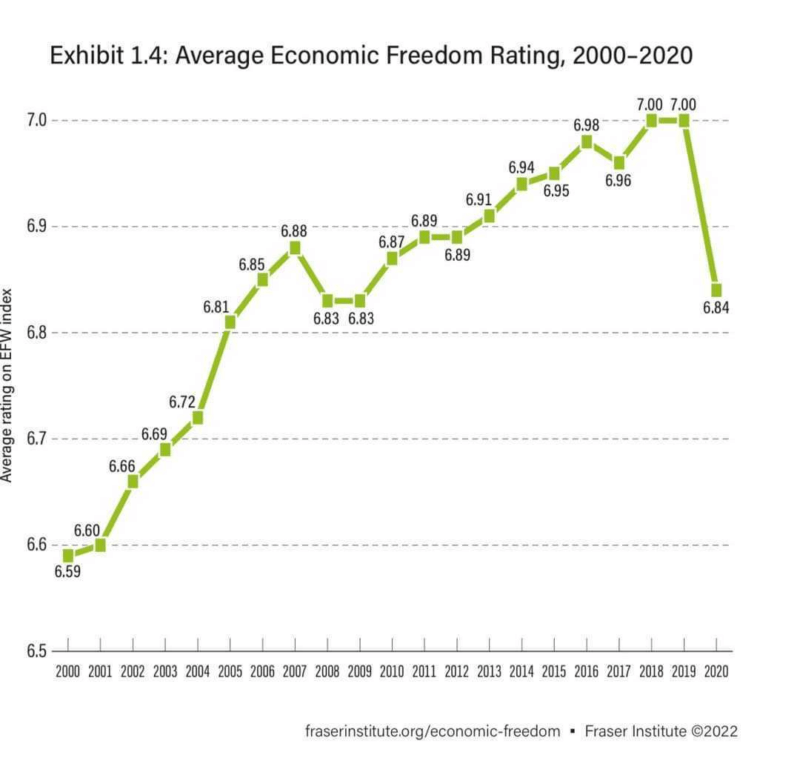
When additional years of data from the COVID era are added, we fully expect that economic freedom around the world will continue to falter. But let’s not get ahead of ourselves. The 2020 data is bad enough. The global average economic freedom rating fell .14 points in 2020, erasing a decade’s worth of improvements.
But first, some notes on what the Fraser Institute measures.
The Economic Freedom of the World report comprises measurements across five categories and 165 jurisdictions: size of government, legal system and property rights, sound money, freedom to trade internationally, and regulation. Perhaps the most important facet of the report is that we can look at the data in absolute terms, asking, for example, how well the United States has been doing over time. We can also look at the data in relative terms, asking how well the United States has been doing compared to the other nations of the world.
We have become accustomed to seeing a steady climb to better lives. Indeed, many of us could not comprehend living as our grandparents did. But thanks to the Fraser Institute, we now have detailed data from 1980-2020, detailing two generations. How do we stack up?
Many will be surprised that the United States is not at the top of the list of most-free countries. In 2020 the US was seventh, behind Hong Kong, Singapore, Switzerland, New Zealand, Denmark, and Australia. And while seventh in the world is nothing to sneeze at, the US trajectory has been downward for quite some time, if only moderately so. In 1980 and 1990, the US was the second economically freest nation in the world. In 2000, it was third. In 2010 and 2015 it was fifth and sixth, respectively. And by 2020, it was seventh.
But that only tells part of the story. It’s when we look at ratings rather than rankings that things get interesting. While the United States has been kicking around in the top ten, even if falling, for decades, it is not doing all that well when compared to itself over time. Indeed, the US’s cumulative rating of 7.97 is considerably lower than its 1980 rating of 8.34. Digging into the recent data, the United States dropped in rank across all five indexed categories from 2019 to 2020. The most significant changes have been in the size of government and regulation categories, where the United States fell 7.32 to 6.79, and 8.68 to 8.11, respectively. Both measures directly reflect the COVID era’s unprecedented expansions of government, as federal spending was unleashed from any semblance of fiscal constraint and draconian regulatory intrusions on daily economic life reached every single American.
In short, the United States finished 2020 less economically free than we were at the tail end of the Carter years.
In the time since COVID, these problems have only continued to compound. The United States appears to be entering the same economic malaise of bloated bureaucracy, excessive taxation, and spiraling inflation that typified the Carter years. Back then we had to wait in line, sometimes for hours, just to buy gas. Now we have rolling blackouts and energy crises in some states, impending electric vehicle mandates, perpetual budget-busting deficits that were unheard of even two decades ago, and – yes – a return of inflation that tops 8 percent for the year. Perhaps the most telling fact of all is that our elected officials and policymakers haven’t a clue how to reverse these trends. Indeed, they are still feeding them.
So where is all this going? Well, 2021 is a full year of COVID lockdowns, so you can bet that data will be worse. We will know then, though, if 2022 shows a reversal of the decline – assuming that the present trends do not continue to compound the problems that COVID lockdowns started.
The real question now is whether we have learned any lessons about economic freedom and lockdowns. These new data provide us an unwelcome warning of what happens when the power of government becomes unmoored from any restraint, but the trend may yet be reversible.