Are you planning to offer your employees a retirement plan for the first time? Or, are you considering switching from a SIMPLE IRA to 401(k)? Whatever the case, you might have questions about the difference between a 401(k) vs. SIMPLE IRA plan. After all, you want to choose the best plan for your business.
Read on to learn about how these two common retirement plan options compare, including contribution limits, employer eligibility, and more.
401(k) vs. SIMPLE IRA
Both SIMPLE (Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees) IRAs (Individual Retirement Accounts) and traditional 401(k) plan options are employee retirement benefits—with key differences.
Here’s a brief overview of the two common retirement plan options:
- 401(k): A 401(k) is a profit-sharing plan that lets employees and employers (if applicable) contribute to an employee’s individual account. Types of 401(k) plans include traditional, safe harbor, SIMPLE, and Roth 401(k)s. Employers must conduct nondiscrimination testing and file annual forms with a traditional 401(k).
- SIMPLE IRA: A SIMPLE IRA lets employees and employers contribute to an employee’s traditional IRA. Small employers can offer this type of retirement plan. Employers do not need to conduct nondiscrimination testing or file annual forms with a SIMPLE IRA.
Sure, the two plans may sound similar at first glance … until you look at contribution limits and employer responsibilities. Read on for a closer look at the difference between SIMPLE IRA and 401(k).
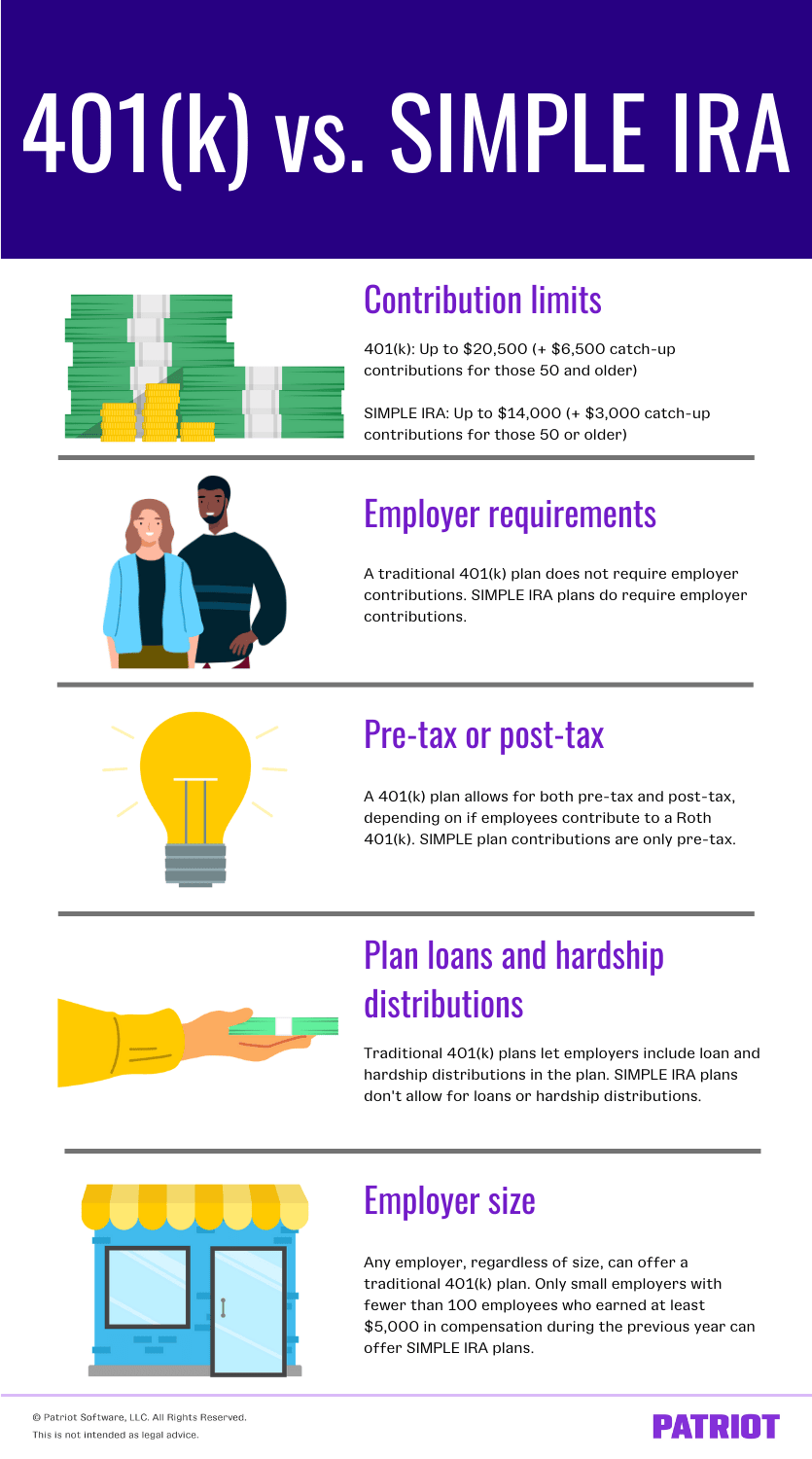
1. How much can employees contribute?
The IRS sets an annual limit on how much employees can contribute to their retirement plan accounts. A SIMPLE IRA and 401(k) have different contribution limits.
A traditional 401(k) plan lets employees contribute more than a SIMPLE IRA plan.
The 2022 401(k) plan contribution limit is $20,500. Employees who are 50 and older can make additional catch-up contributions of $6,500.
The 2022 SIMPLE IRA plan contribution limit is $14,000. Employees who are 50 and older can make additional catch-up contributions of $3,000.
2. Do employers have to contribute?
Offering a retirement plan option is a great way to boost your employee benefits. But, do you have to contribute money, too? Yes—depending on the plan you go with.
A traditional 401(k) plan does not require employer contributions. SIMPLE IRA plans do require employer contributions.
SIMPLE IRA plans generally require that employers match each employee’s contribution on a dollar-for-dollar basis, up to 3% of the employee’s compensation. All employer contributions immediately vest, meaning the employee owns them.
Traditional 401(k) plans do not require employer contributions. However, you can choose to do so. If you do contribute, you can subject employer contributions to a vesting schedule (e.g., 50% vested after one year). Keep in mind that other types of 401(k) plans, such as a SIMPLE 401(k) plan, require employer contributions.
3. Are contributions pre-tax or post-tax?
All retirement plan benefits are taxed—eventually. But, there are both pre-tax and post-tax deductions for retirement. Pre-tax contributions mean the amount is not part of the employee’s taxable income. The employee then pays taxes on distributions (aka, when they withdraw money for retirement). Post-tax contributions mean the amount is part of the employee’s taxable income. The employee does not pay taxes on distributions. Which is which?
SIMPLE plan contributions are only pre-tax. A 401(k) plan allows for both pre-tax and post-tax, depending on if employees contribute to a Roth 401(k).
If you want to give employees the option of pre-tax or post-tax contributions, you may consider a 401(k) plan.
4. Can employees take out a loan or receive hardship distributions?
Some employers allow employees to take out a loan or receive a hardship distribution from their retirement plan. This lets employees borrow or withdraw funds from their accounts. But, not all retirement plans have this feature.
SIMPLE IRA plans don’t allow for loans or hardship distributions. Traditional 401(k) plans let employers include loan and hardship distributions in the plan.
Sure, retirement plans are meant to be tucked away until, well, retirement. But things happen. And if an employee wants to take out a loan or receive a hardship distribution from their SIMPLE IRA, they’re out of luck.
5. Can all employers offer them?
The last difference between a 401(k) vs. SIMPLE IRA is a big one: Who can offer the plan?
Any employer, regardless of size, can offer a traditional 401(k) plan. Only small employers can offer SIMPLE IRA plans.
You can offer a SIMPLE IRA if you have fewer than 100 employees who earned at least $5,000 in compensation during the previous year.
If your business is growing, congratulations! But, it might be time to switch your SIMPLE IRA to 401(k).
Interested in a 401(k)?
Although SIMPLE IRAs are easy to offer, a 401(k) plan provides more flexibility for business owners.
If you’re thinking about switching from a SIMPLE IRA to a 401(k), consider:
- Deadlines: You can amend or change your SIMPLE IRA at the beginning of the year (January 1). However, you must provide a 60-day notice to employees before terminating your SIMPLE IRA. So, you must inform employees of any plan changes by November 2.
- Providers: Patriot has partnered with Vestwell to offer payroll with seamless 401(k) integration. You can learn more about switching to a 401(k) plan with Vestwell here.
Want to make offering 401(k) plans easier? Patriot’s payroll software makes it easy to withhold taxes and other deductions, like retirement contributions. And thanks to our upcoming partnership with Vestwell, we now offer payroll with seamless 401(k) integration.
This is not intended as legal advice; for more information, please click here.


