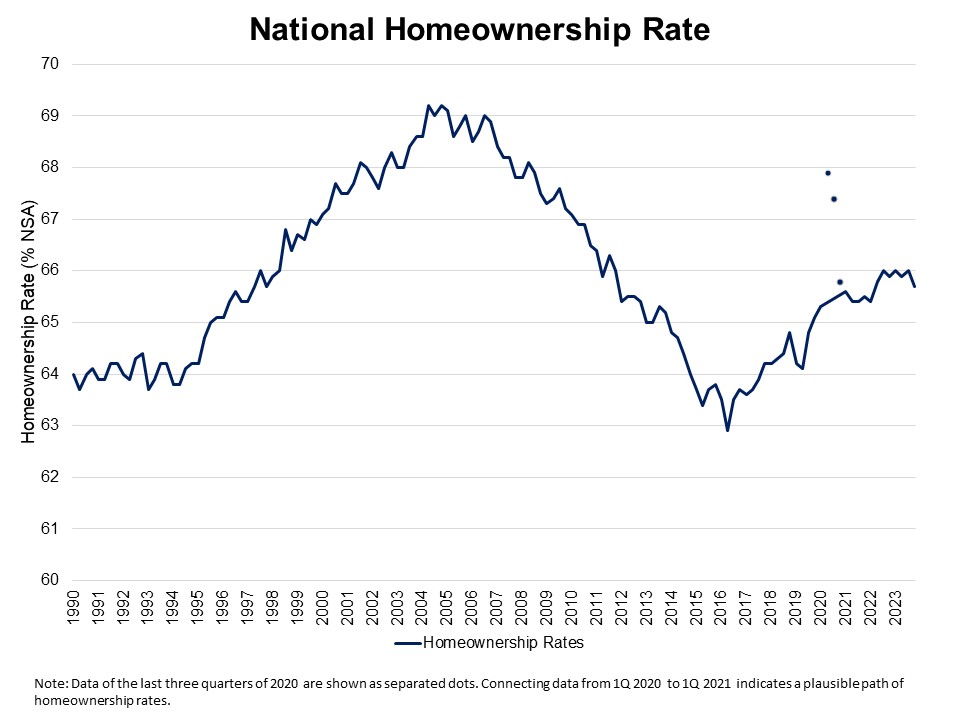
The Census Bureau’s Housing Vacancy Survey (CPS/HVS) reported the U.S. homeownership rate declined to 65.7% in the last quarter of 2023, amid persistently tight housing supply and elevated mortgage interest rates. This is 0.3 percentage points lower from the third quarter reading (66%). Compared to the peak of 69.2% in 2004, the homeownership rate is 3.5 percentage points lower and remains below the 25-year average rate of 66.4% amid a multidecade low for housing affordability conditions.
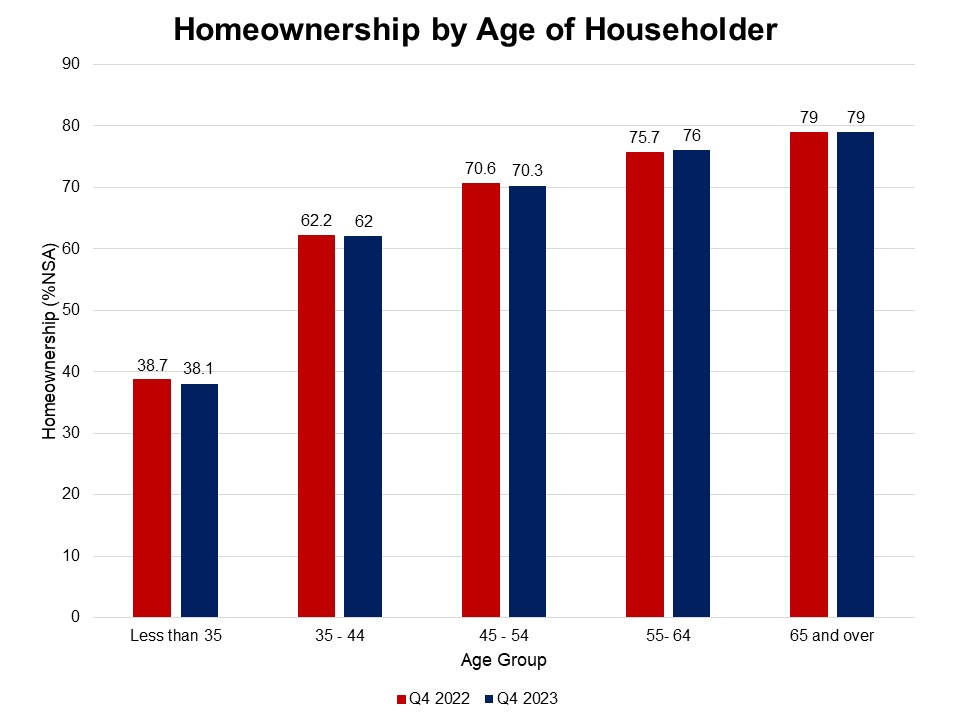
The homeownership rate for householders aged less than 35 decreased to 38.1% in the fourth quarter of 2023, as affordability is declining for first-time homebuyers amidst elevated mortgage interest rates and tight housing supply. This age group, particularly sensitive to mortgage rates and the inventory of entry-level homes, saw the largest decline among all age categories.
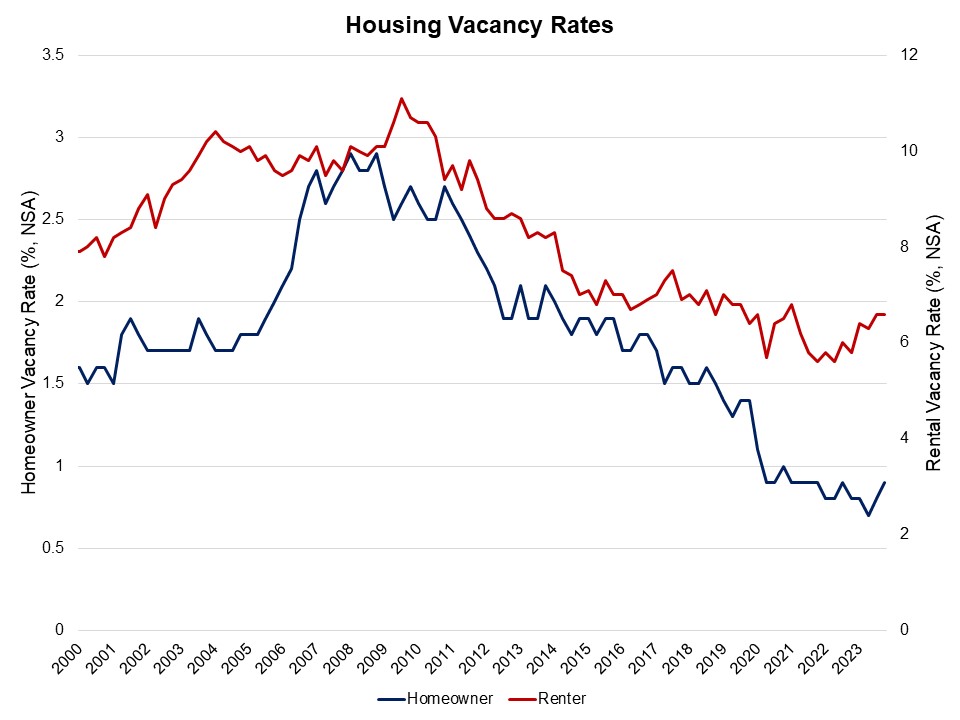
The national rental vacancy rate stayed at 6.6%, and the homeowner vacancy rate inched up to 0.9% from 0.8%. The homeowner vacancy rate is still hovering near the lowest rate in the survey’s 67-year history (0.7%).
The homeownership rates of adults in all age groups decreased over the last year, except those aged 55-64 and 65 years and over. The homeownership rates among householders aged less than 35 experienced a 0.6 percentage point decrease, from 38.7% to 38.1%, followed by the 45-54 age group with a 0.3 percentage point decrease from 70.6% to 70.3%. Next, were households aged 35-44, who experienced a modest 0.2 percentage point decline. However, homeownership rates of householders aged 55-64 showed an increase of 0.3 percentage points.
The housing stock-based HVS revealed that the count of total households increased to 131.2 million in the fourth quarter of 2023 from 129.7 million a year ago. The gains are largely due to modest gains in owner household formation (772,000 increase), while renter households increased 694,000.